Ancient Roman Armor Comes to Life
Experts reconstructed an ancient Roman arm guard that’s nearly 2,000 years old.

© Duncan McGlynn, Courtesy National Museums Scotland
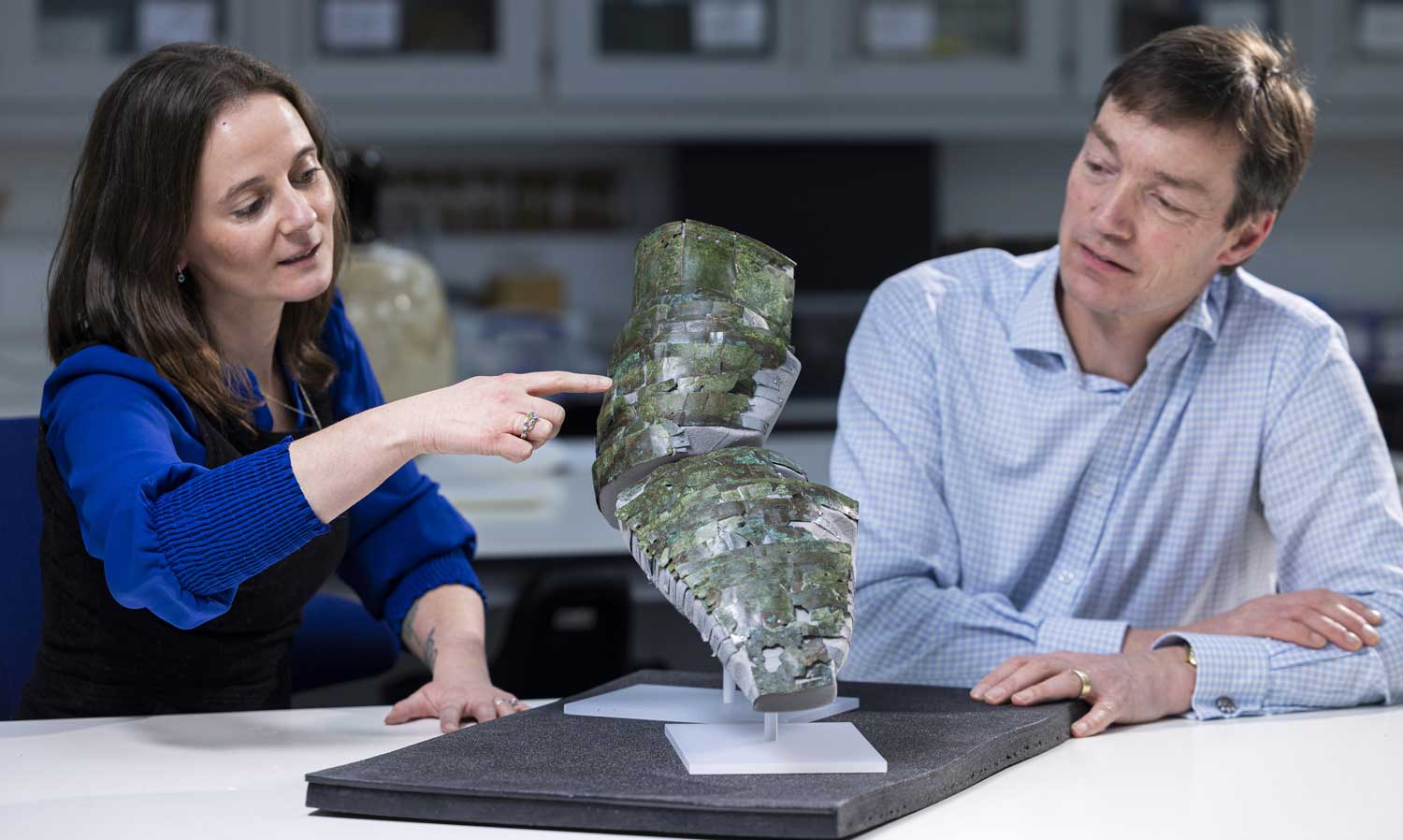
Conservator Bethan Bryan (left) and curator Dr. Fraser Hunter with an ancient Roman arm guard Bryan helped reconstruct from more than 100 pieces.
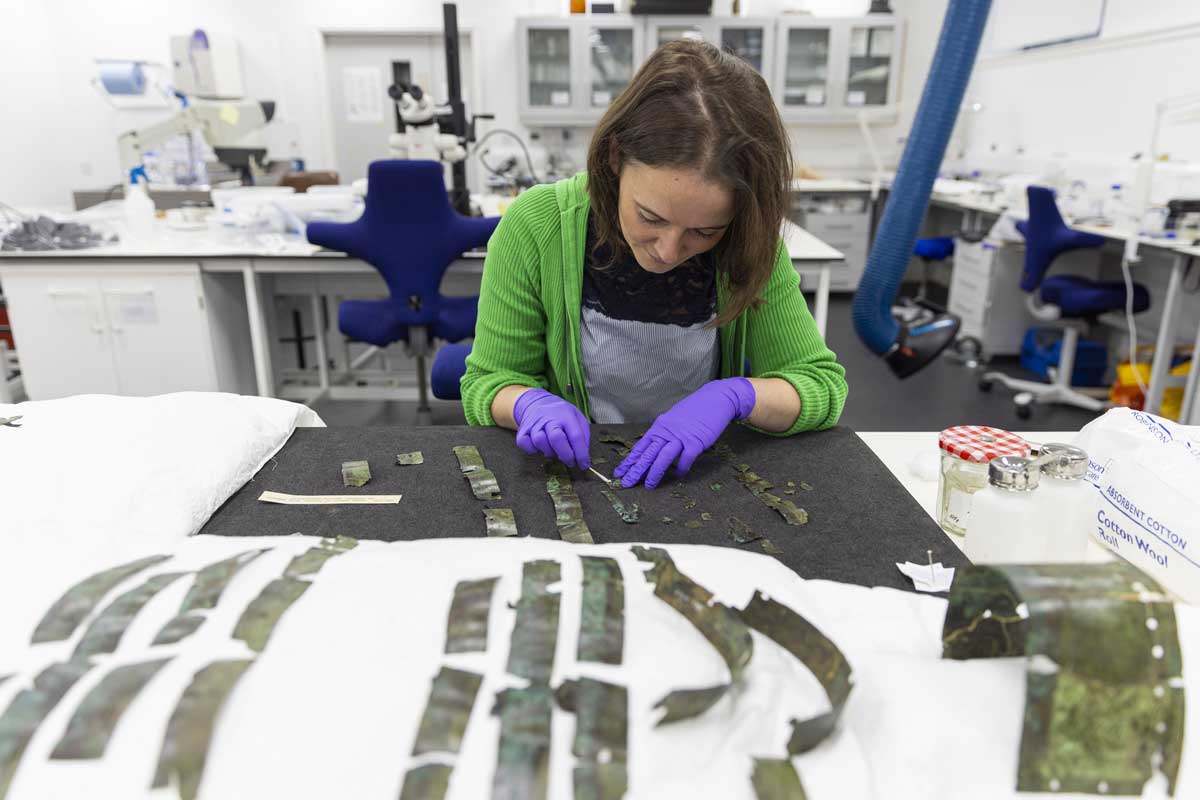
Thousands of years ago, the Roman Empire ruled over much of Europe and North Africa—and maintained its power with the help of armed soldiers. Now, a piece of Roman armor that was discovered in more than 100 pieces in Scotland has been reconstructed.
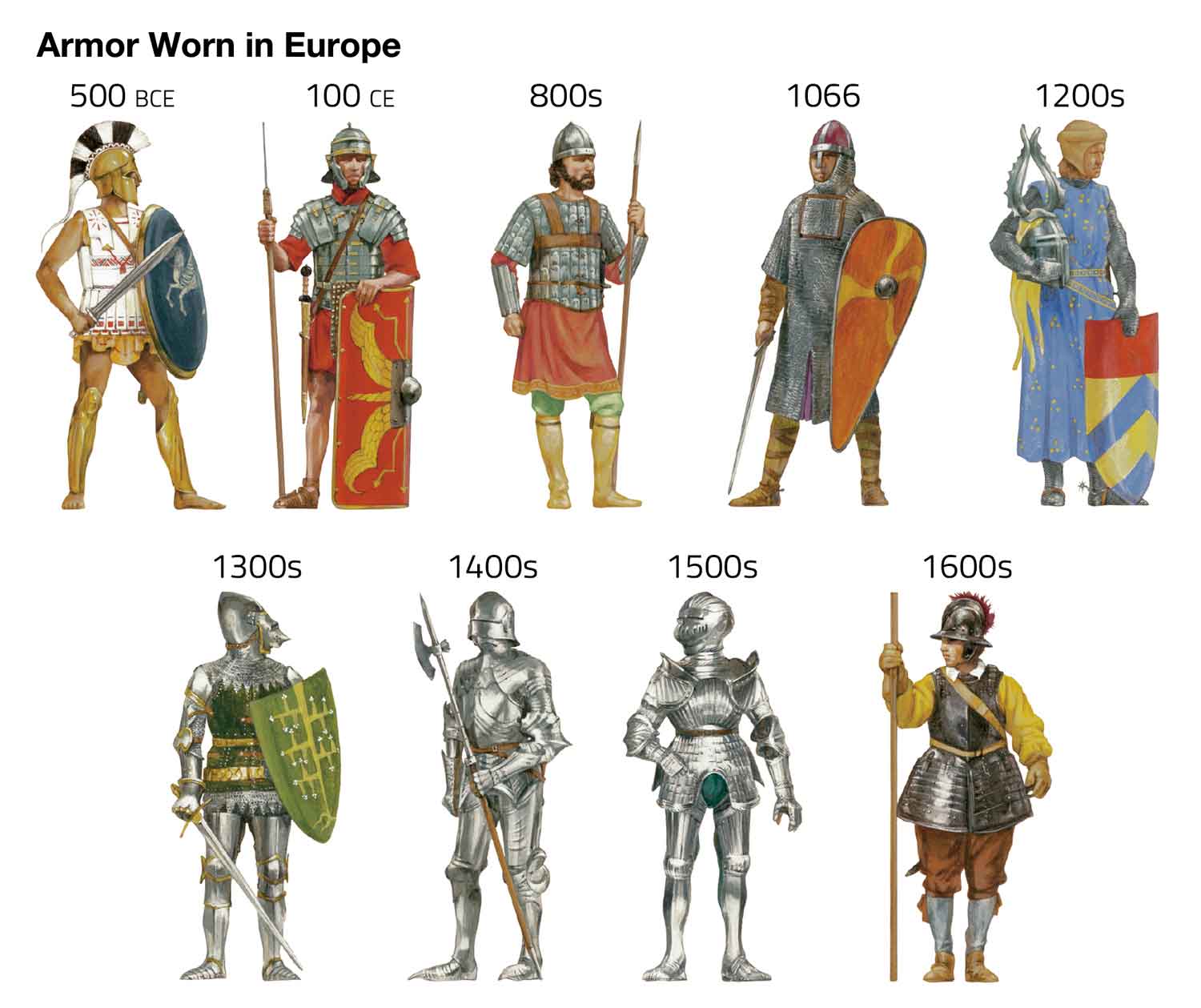
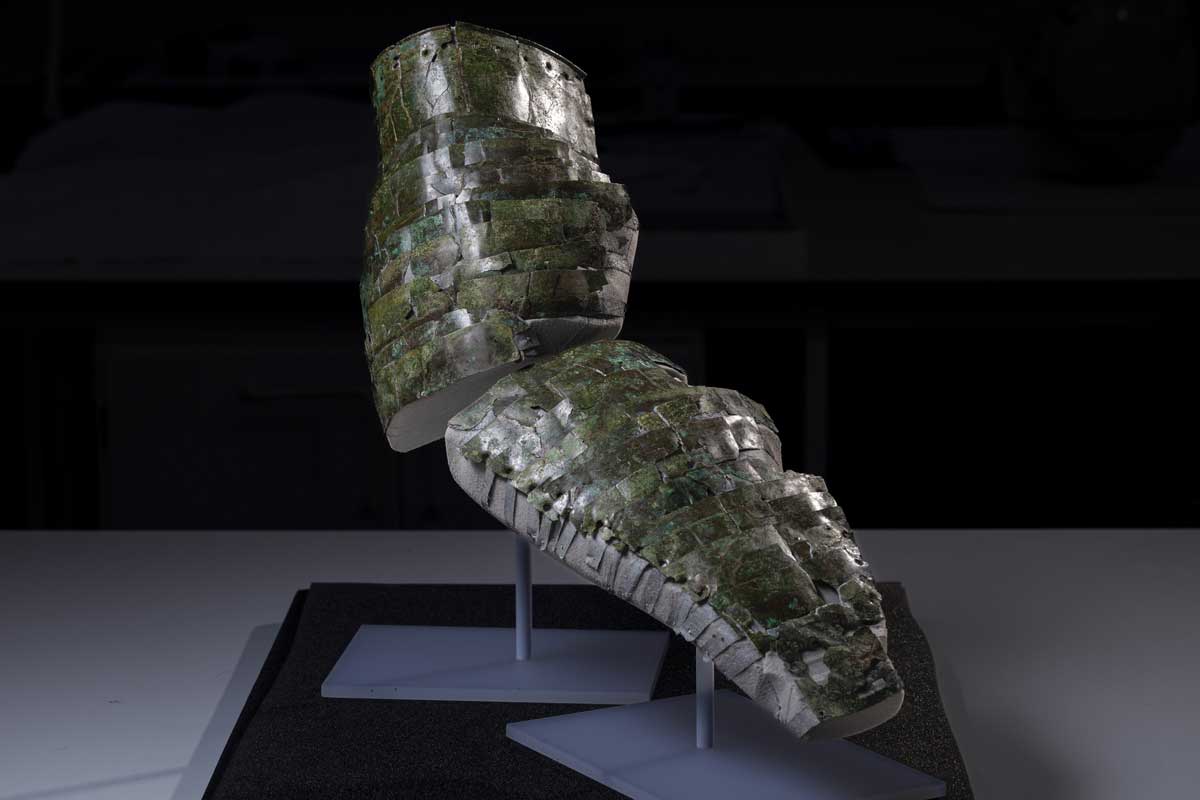
The arm guard was designed to be worn on the right arm of a soldier as he held a sword in that hand. The metal, along with attached leather padding, would have helped cushion blows from enemy weapons. Experts say that, while most arm guards were made of less expensive and more durable iron, this one was made of brass, suggesting that its owner was of a high military rank.
“It’s absolutely amazing. You get the sense of the protection this person had—and also the prestige,” Fraser Hunter of National Museums Scotland told the Observer. “It would have gleamed gold and would have looked absolutely spectacular when he was wearing it.”



© Duncan McGlynn, Courtesy National Museums Scotland
Richard Abdy, an expert on ancient Roman coins from the British Museum, noted that this style of arm guard would more commonly be worn by gladiators—men who were trained to fight other men or animals in arenas for public entertainment.
“The flexible arm guard is an iconic piece of equipment for Roman gladiators, so it is unusual to see it as a sword-arm protection for Roman soldiers, too,” Abdy said in a statement.
The arm guard was discovered in 1906 by British archaeologist James Curle at the site where a Roman military fort called the Trimontium once stood. The Romans attempted to conquer Scotland, but the local people fought back. The Romans left the area in about 180 CE due to violence and unrest—and abandoned the fort with the arm guard and other artifacts inside.
The arm guard is now on display at the British Museum in London, England, as part of an exhibit called “Legion Life in the Roman Army.” It will later be on permanent display at the National Museum of Scotland in Edinburgh, Scotland.